Trigger Finger
Understanding Trigger Finger: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Introduction:
Have you ever experienced a painful, locking, or popping sensation in one or more of your fingers when trying to bend or straighten them? If so, you might be dealing with a condition called "Trigger Finger." In this article, we'll explore what trigger finger is, its common causes, symptoms, and available treatment options to help you better understand and manage this condition.
What Is Trigger Finger?
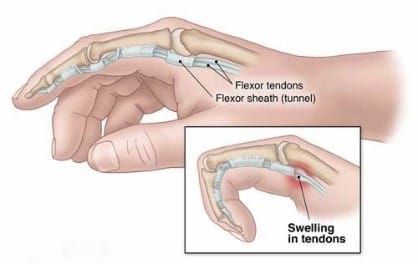
Trigger Finger, medically known as stenosing tenosynovitis, is a condition that affects the tendons in your fingers or thumb. It occurs when the affected tendon becomes inflamed or swollen, making it difficult for the tendon to glide smoothly within its protective sheath, resulting in a clicking or catching sensation when you move your finger.
Common Causes of Trigger Finger
While the exact cause of trigger finger can vary from person to person, there are several common factors and risk factors associated with its development:
- Repetitive Hand Movements:Engaging in repetitive hand or finger movements, such as typing, gripping tools, or playing musical instruments, can increase the risk of developing trigger finger.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout can make you more susceptible to trigger finger.
- Age and Gender: Trigger finger is more common in women and individuals over the age of 40.
Recognizing the Symptoms
The symptoms of trigger finger typically progress gradually and may include:
- Finger Stiffness: Difficulty in straightening or bending the affected finger.
- Popping or Clicking Sensation: When moving the finger, you may feel a popping or clicking sensation.
- Pain or Tenderness: Pain at the base of the finger or thumb, which may worsen with movement or pressure.
- Finger Locking: The finger may get stuck in a bent position (triggered) and require manual straightening.
Treatment Options:
-
1. Conservative Approaches:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Reducing or modifying activities that trigger symptoms can provide relief.
- Hand Splinting: Wearing a splint to immobilize the affected finger can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended to reduce pain and inflammation.
2. Corticosteroid Injections:
In some cases, a healthcare provider may administer corticosteroid injections into the affected area to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
3. Physical Therapy
In more severe cases, traditional open surgery may be necessary to release the constricted sheath.
Preventing Trigger Finger
While some risk factors for trigger finger, like age and gender, cannot be controlled, you can take steps to reduce your risk and prevent its recurrence:
- Ergonomic Practices: Maintain proper hand and wrist positioning when engaging in repetitive tasks.
- Stretching Exercises: Regularly perform hand and finger stretches to maintain flexibility.
- Rest and Recovery: Allow your hands and fingers adequate time to rest and recover after strenuous activities.
Conclusion
Trigger finger is a common condition that can affect your daily activities and quality of life. If you suspect you have trigger finger or are experiencing symptoms, seek medical advice promptly. With proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment, you can manage the condition effectively and regain full use of your fingers or thumb. Early intervention is key to a successful recovery.
Contact Us
Dr. Jawad Khan
Phone: 714-435-9909
Fax: 714-435-9910
8740 Warner Ave
Fountain Valley, CA 92708
Private Insurances Accepted
- PPO
- EPO
- Medicare
- Medicare + Secondary Insurance
- Worker’s Compensation
- Tri-Care PPO