Ganglion Cyst of the Wrist Excision
Understanding Ganglion Cysts of the Hand and Wrist: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
However, if the cyst becomes painful or interferes with hand movement, they can be treated non-surgically or removed surgically.
Introduction
Have you ever noticed a small lump or bump on your hand or wrist that seems to appear out of nowhere? This may be a ganglion cyst, a common condition that affects many individuals. In this article, we'll explore what ganglion cysts are, their common causes, symptoms, and available treatment options to help you better understand and manage this condition.
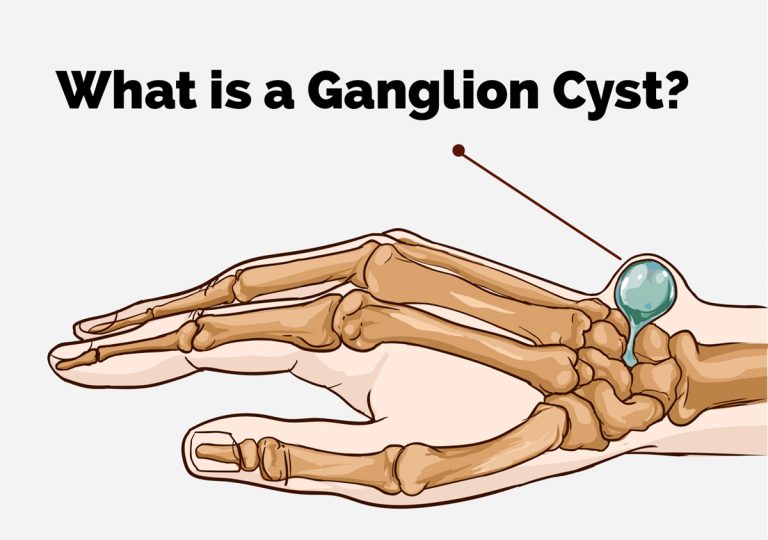
What Are Ganglion Cysts?
Ganglion cysts, often referred to as "Bible cysts" in the past due to a common treatment method, are noncancerous, fluid-filled sacs that typically develop near joints or tendons, most commonly in the hand or wrist. These cysts can vary in size, and while they are generally harmless, they can cause discomfort or limited range of motion.
Common Causes of Ganglion Cysts
The exact cause of ganglion cysts is not always clear, but several common factors and risk factors may contribute to their development:
Conservative treatment options
In many cases, ganglion cysts disappear without any treatment. If bothersome, your doctor make recommend wearing a wrist brace or splint to immobilize the area and allow the cyst to shrink.
- Joint or Tendon Irritation: Repetitive stress or injury to a joint or tendon can lead to the formation of a ganglion cyst.
- Connective Tissue Disorders: Certain conditions, such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, may increase the likelihood of developing ganglion cysts.
- Age and Gender:Ganglion cysts are more prevalent in women and individuals between the ages of 20 and 40.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Ganglion cysts can present with a range of symptoms, including:
- Lump or Bump: A noticeable lump or bump that is often round and firm. It may be accompanied by tenderness.
- Pain: Discomfort or pain, especially when the cyst presses on nearby nerves or tissues.
- Change in Size: The size of the cyst may fluctuate over time, and it may become larger with increased activity.
- Limited Range of Motion: In some cases, the cyst's location can restrict the movement of nearby joints or tendons.
Diagnosis and Treatment
If you suspect you have a ganglion cyst, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis. They may perform a physical examination and may recommend imaging tests, such as ultrasound or MRI, to confirm the presence and location of the cyst.
Treatment Options:
- Watchful Waiting: In many cases, ganglion cysts do not require immediate treatment. Your doctor may recommend monitoring the cyst for changes and only intervening if it causes pain or discomfort.
- Aspiration: A healthcare provider can use a needle and syringe to drain the fluid from the cyst. This is often combined with a corticosteroid injection to reduce inflammation.
- Splinting: Wearing a splint or brace to immobilize the affected joint can help reduce pain and prevent the cyst from returning.
- Surgery: In cases where the cyst is causing persistent pain or limiting function, surgical removal may be recommended. This procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia.
Preventing Ganglion Cysts
While ganglion cysts cannot always be prevented, you can take certain precautions to reduce your risk:
- Protect Your Joints: Use protective gear when engaging in sports or activities that put your wrists and hands at risk of injury.
- Protect Your Joints: Use protective gear when engaging in sports or activities that put your wrists and hands at risk of injury.
- Early Intervention: If you notice a lump or experience pain, seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications.
Conclusion
Ganglion cysts are common benign growths that can occur in the hand or wrist, and they are usually not a cause for concern. However, if you have any concerns or experience pain or discomfort, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and guidance on the best treatment approach. With proper care, you can effectively manage ganglion cysts and maintain the health and function of your hand and wrist.
Contact Us
Dr. Jawad Khan
Phone: 714-435-9909
Fax: 714-435-9910
8740 Warner Ave
Fountain Valley, CA 92708
Private Insurances Accepted
- PPO
- EPO
- Medicare
- Medicare + Secondary Insurance
- Worker’s Compensation
- Tri-Care PPO